Cannabinoids - The Basics
Have you ever taken the time to glance at the label of any medication that you can purchase over the counter? If yes, then you have probably noticed that there is a list of active ingredients.

Those active ingredients are what give medications their ability to treat the symptoms of many different ailments.
The majority of the “active ingredients” in cannabis are referred to as cannabinoids.
As of the time of this writing, almost 150 phytocannabinoids have been discovered and more are certain to be found as research continues. The first phytocannabinoid to be discovered was CBN. It was explained in the early 1930s by British chemist Robert S. Cahn when he discovered the partial structure of CBN. Later in 1940, he identified CBN as fully formed.
The most recent phytocannabinoids (as of publishing) to be discovered in cannabis include cannabidiphorol (CBDP) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiphorol (Δ9-THCP) which were discovered in late 2019.
Understanding the basics of cannabinoids is important for your overall knowledge of medical cannabis and can also help inform you when you are trying to make the best possible choices for your individual medical cannabis program.
What are Cannabinoids?
According to WebMD, cannabinoids are defined as:
the active chemicals in medical marijuana -- are similar to chemicals the body makes that are involved in appetite, memory, movement, and pain.
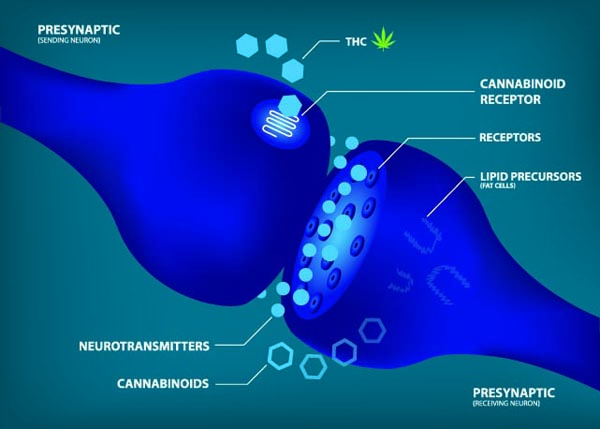
If you look closely at this definition, you will notice that it mentions cannabinoids are “similar to chemicals the body makes.” Yes, we all have similar compounds to cannabinoids in our bodies naturally. This internal system is referred to as the “Endocannabinoid System.”
To learn more about the Endocannabinoid System, we invite you to check out our Kanteeva article by following this link.
For the purposes of this article, we are going to focus on what are called phytocannabinoids, aka the cannabinoids that are found in the cannabis plant. Most of the time when you hear someone reference cannabinoids, this is what they are talking about.
Phytocannabinoids - the Inactive Ingredients of Cannabis

Believe it or not, in its raw form, cannabis does not possess activated cannabinoids. Instead, raw cannabis contains what are called cannabinoid acids.
These acids are naturally created in the cannabis plant and are “activated” when they lose their acid via decarboxylation. Not 100% of cannabinoids are “activated,” so when we consume cannabis we also consume the non-activated cannabinoid acids.
Little research has been completed on these cannabinoids acids, although many experts believe they will have immense medical benefits when harnessed properly.
Contrary to what pop-culture movies would have you believe, eating an entire bag of raw cannabis will not produce the psychoactive “super high” that is often portrayed in mainstream culture.
Cannabinoid acids have unique benefits too and we are just starting to realize what some of these potential medical benefits are. For example, THCA is used by some people as a dietary supplement, via the ingestion of raw cannabis, and they claim that THCA can be effective for helping to treat many ailments. Recent research also suggests that CBDA is a superior anti-emetic when compared to the activated versions THC and CBD.
Cannabinoid acids are starting to gain traction in niche medical and health communities around the world. Unfortunately, most of the information is anecdotal and more clinical trials must be completed in order to understand and unlock the medical benefits of all forms of cannabinoids.
So, How do Cannabinoid Acids Become Cannabinoids?
In essence, all that is needed is heat. The process of activating the cannabinoid acids is typically known as “decarboxylation.” Once raw cannabis has been decarboxylated, cannabinoids like THC and CBD will be available for our bodies to utilize through our Endocannabinoid System.
Below are the cannabinoids that are typically the most prevalent in cannabis at relatively high concentrations.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
Perhaps the most famous cannabinoid, THC is the most prevalent cannabinoid in most modern cannabis strains. It is the psychoactive cannabinoid responsible for getting you “high” and is used for treating many symptoms of ailments like neuropathic pain, spasticity, and loss of appetite, just to name a few.
To learn more about THC, we invite you to read our article “What is THC?”.
CBD (Cannabidiol)
The second most prevalent cannabinoid in most strains and the main cannabinoid in some special medical strains, CBD has received tons of media attention in recent years for its many medical and health applications.
This cannabinoid is non-psychoactive and consuming CBD will not get you high, but it has shown promise at helping to relieve a variety of symptoms for many common ailments. While many people report having success using CBD for symptoms ranging from chronic pain to migraine prevention, modern medical research has shown that CBD is beneficial for helping to control seizures, especially in rare cases of pediatric epilepsy.
Check out our “What is CBD?” article for more information.
CBN (Cannabinol)
Unlike the other cannabinoids on this list, CBN does not occur in a cannabinoid acid form in living cannabis plants. Instead, this cannabinoid is created when THCA (the acid form of THC contained in raw cannabis) begins to break down after being exposed to oxygen or ultraviolet light. Once this process begins, CBNA (the acid form of CBN) is created and once it is decarboxylated, CBN is formed. While there has not been a significant amount of research done on CBN, it is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid that shows preliminary promise of relieving the symptoms of ailments like insomnia, inflammation, bone cell growth and more.
Check out our “What is CBN?” article for more information.
CBG (Cannabigerol)
Like most cannabinoids, there has been little research conducted on CBG. However, early research shows promise that CBG may have properties that can help relieve symptoms associated with colitis, inflammatory bowel disease and loss of appetite. Like CBD, early studies on CBG show that it does not have any psychoactive effects associated with its use.
CBGA is the precursor cannabinoid that enables the biosynthesis of THC, CBD and CBC. It is most prevalent in the cannabis plant during the middle of the flowering phase (4 to 6 weeks after initial flowering begins).
CBC (Cannabichromene)
Another cannabinoid that lacks sufficient research, CBC has shown promise in early studies for helping to treat the symptoms of ailments like neurological disorders, movement disorders, pain and inflammation. No psychoactive effects are known to be associated with the consumption of CBC.
An Important Need for Research

Remember when we were talking at the beginning of this article about the active ingredients being shown on most medication bottles? Well, imagine finding a bottle that listed close to 150 active ingredients.
This is the potential that cannabis may have.
There is still tons of medical and scientific research to be done before we truly understand what each cannabinoid does. As of now, modern science is just starting to scratch the surface on the possible medical benefits that different cannabinoids could have.
Thankfully, more research is being conducted into cannabinoids and many people are hopeful that in the near future we will unlock more of the secrets that these unique compounds hold.
For now, we can only rely on the existing research that has been conducted, as well as the patient testimonials from thousands of people who have found relief through medical cannabis.
Final Thoughts
Hopefully, after reading this article, you now have a more thorough understanding of cannabinoids.
If you still feel a little confused, it’s okay. Remember that up until just a few years ago, many people believed that cannabis had no medicinal benefits. Now, we are discovering that the active ingredients of cannabis known as cannabinoids may potentially deliver a myriad of health benefits for people who are suffering from various ailments.
If you have any additional questions about cannabinoids, please leave them below and a member of the Kanteeva staff will respond back to you.
Also, be sure to join the Kanteeva community to stay up-to-date with the latest information on cannabinoid and cannabis research, what other members are finding success with and for more information to help you determine your best cannabis therapy options.
Learn. Share. Connect.